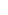
33.Pair of ear ornaments

- ca. 1st century BCE–1st century
- Attributed to Andhra Pradesh
- The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York
This spectacular pair of earrings is a rare survival of ancient Indian goldsmithing, much of which was repurposed by later generations. Double-ended tendrils such as these, passed through distended earlobes, are referred to in the ancient Sanskrit epic Mahabharata as being worn by the hero Arjuna while in female disguise. The same style of jewelry is frequently depicted in early Sātavāhana sculpture. Together with gemstone and ivory carvers, potters, and weavers, goldsmiths were an important part of early India's craft guild structure, and inscriptions often name them as donors to Buddhist causes. The only other examples of this ear ornament type were recovered in the Thai peninsula, an indication of early Sātavāhana trade with Southeast Asia.

 Previous
Previous